
NEWS
CONTACT US
NEWS
Home > NEWS

Filter cloth is increasingly applied by more and more industries such as chemicals, metallurgy, mining, food & drinks and pharmacy as an effective and affordable media of solid-liquid separation. As an essential factor of filter machines,(such as filter press, belt filter, disc filter,etc.) filter cloth plays an important role to ensure clear filtration, dry filter cake, short filter cycle and long lifetime.
There are 3 ways of cloth type selection.
1. If your present filter cloth is satisfactory and you have filter cloth specifications, we will choose equivalent according to the specifications. This is the most simple and efficient way. Our sample will be sent for your confirm.
2. If you have cloth sample, you can send to us for analysis. We will choose equivalent type. This will increase the accuracy of cloth type.
3. If you can send us the filtrate solid, we can make filtration test and choose the most suitable type. This is the most correct way of choosing type.
The following are the details factors that affect the cloth type selections.
· Materials
· Yarn Types
· Weave Patterns
·
Materials
Polyester (PE) filter cloth
The prominent property for polyester fabric is its strongest acid resistance among existing synthetic fabrics. It is widely recognized as an outstanding and popular filter cloth for its high operating temperature up to 150 degree , high tensile strength and good elongation.
Polypropylene fabric
Polypropylene fabric is characterized by sleekness, excellent permeability and little moisture absorption. Its excellent cake release will significantly shorten cleaning time as well as filter cycle. It also has excellent resistances against most acids and alkalis. Its constant working temperature is rated at 90 degree. It is resistance of PH 14 high alkali, so it is preferred by the aluminum factory for the alumina filtration.
Nylon filter cloth
Nylon filter cloth features optimum abrasive resistance and strong alkali resistance. It is often found in miner and coal industries for its best abrasion proof. The only shortage is that its chemical instability under high and low temperature. Under high temperature, the cloth will extend, and under low temperature, it will shrink. Another important feature for nylon is under the high temperature, it will release toxic substance and pollute the solutions. So, nylon filter cloth is not accepted by food & beverage and pharmaceutical.
Properties of Frequently Used Filter Fabrics
Property | Polyester (PE) | Polypropylene | Nylon |
Acid | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Alkali | Average | Excellent | Excellent |
Electrical Conductivity | Poor | Good | Average |
Elongation | 30%-40% | Better than PE | Poor |
Recovery | Excellent | Slightly better than PE | Poor |
Abrasion | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Heat Resistance | 150 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C |
Softening point | 230 -240 °C | 140 -150 °C | 200 °C |
Melting point | 255 -265 °C | 165 -170 °C | 220 °C |
Yarn Types
Multifilament Yarn

Multifilament yarn is twisted together by monofilament yarns. The cloth fabricated by multifilament yarns has a smooth surface, high tensile strength, average particle collection efficiency and cake release.
Monofilament Yarn
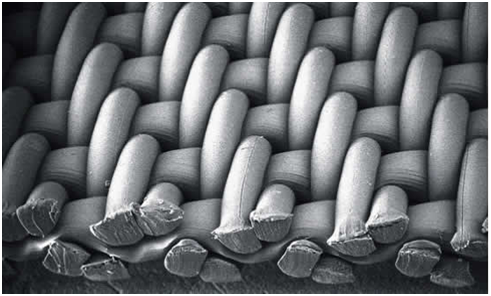
Monofilament yarn is single and continuously extruded from synthetic resin. It has excellent cake release, resistance to blinding and low particle collection efficiency.
Staple (spun) yarn
Staple yarns are fabricated of chopped filaments. These short fibers have low tensile strength, a large surface area. Staple fabric has poor cake release but excellent particle retention.
Weaving pattern
Plain weave

Plain weave is the most basic of three fundamental types of textile weaves (along with satin weave and twill). It is strong and hard-wearing. In plain weave, the warp and weft are aligned so they form a simple criss-cross pattern. Each weft thread crosses the warp threads by going over one, then under the next, and so on.
The characteristics include high particle retention and low resistance to blinding with average cake release properties.
Twill weave
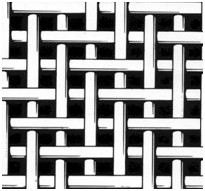
The twill weave is characterized by a diagonal rib, or twill line. Each warp floats over at least two or more consecutive fill yarns, enabling a greater number of yarns per unit area than a plain weave, while not losing a great deal of fabric stability. Characteristics include an average resistance to blinding, average cake release, and good mechanical strength.
Satin weave
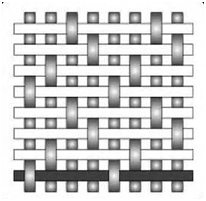
The face of the satin weave fabric consists almost completely of warp produced in the repeat of the weave. This is the most flexible of weave patterns and conforms very easily around most contoured surfaces. Satin weaves are usually four, five, eight, or twelve harness. Characteristics include excellent cake release, average retention, and excellent resistance to blinding.